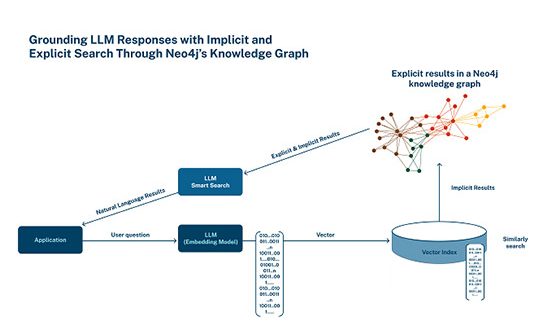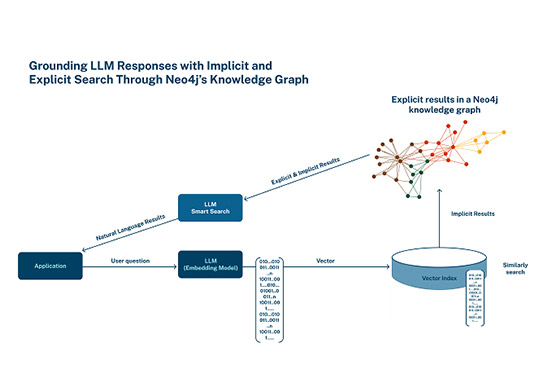
Neo4j has announced it has integrated native vector search as part of its core database capabilities. Neo4j says the result enables customers to achieve richer insights from semantic search and generative AI applications, and serve as long-term memory for LLMs, all while reducing hallucinations.
Neo4j’s graph database can be used to create knowledge graphs, which capture and connect explicit relationships between entities, enabling AI systems to reason, infer, and retrieve relevant information effectively.
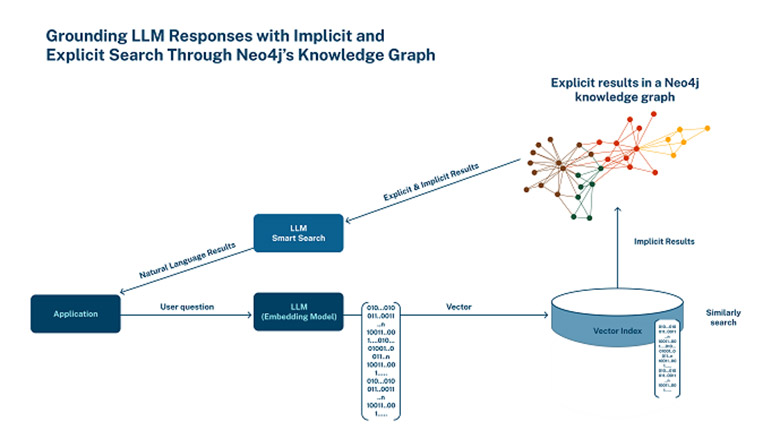
The result ensures more accurate, explainable, and transparent outcomes for LLMs and other generative AI applications. By contrast, vector searches capture implicit patterns and relationships based on items with similar data characteristics, rather than exact matches, which are useful when searching for similar text or documents, making recommendations, and identifying other patterns.
“We see value in combining the implicit relationships uncovered by vectors with the explicit and factual relationships and patterns illuminated by graph,” said Emil Eifrem, Co-Founder and CEO, Neo4j. “Customers when innovating with generative AI also need to trust that the results of their deployments are accurate, transparent, and explainable. With LLMs evolving so dynamically, Neo4j has become foundational for enterprises seeking to push the envelope on what’s possible for their data and their business.”
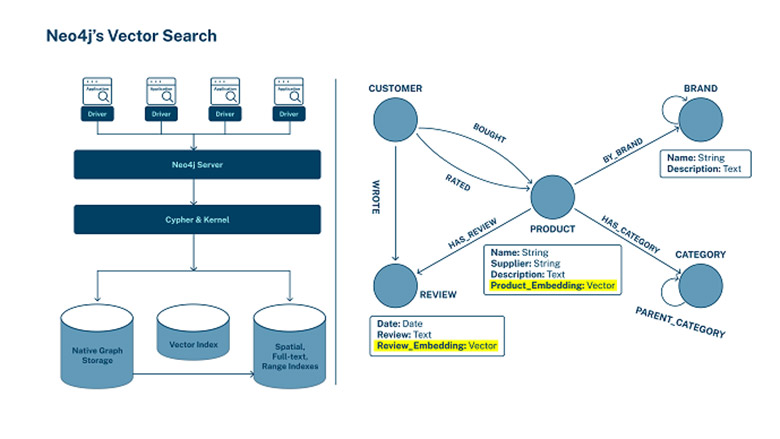
The June 2023 Gartner report, AI Design Patterns for Knowledge Graphs and Generative AI, states that “Knowledge graphs provide the perfect complement to LLM-based solutions where high thresholds of accuracy and correctness need to be attained.”
This latest advancement follows from Neo4j’s recent product integration with Google Cloud’s generative AI features in Vertex AI in June, enabling users to transform unstructured data into knowledge graphs, which users can then query using natural language and ground their LLMs against factual set of patterns and criteria to prevent hallucinations.
Neo4j’s native graph database became fully integrated with Microsoft Azure in April 2023. In December 2022, the company was recognised for the first time in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Cloud Database Management Systems, which was the first time that native graph vendors were included.